What is Managed Detection and Response (MDR)?
Managed detection and response (MDR) is a cybersecurity service and a proactive approach that combines advanced technology and human expertise to monitor endpoints, networks, and cloud environments 24/7. The goal focuses on detecting and responding to cyberthreats using a combination of expertise, processes, and advanced technology to reduce risk and enhance security operations.
Key features include:
- continuous monitoring
- proactive threat hunting
- guided response and remediation
How MDR Fills the Gaps from Traditional Services
MDR services have evolved significantly to keep pace with the changing cybersecurity landscape, integrating advanced technologies and techniques to provide comprehensive protection against sophisticated threats. Unlike traditional security services, MDR offers proactive threat hunting, rapid incident response, and round-the-clock monitoring to address the shortcomings of conventional security measures.
Traditional cybersecurity services, like managed security service providers (MSSPs), typically focus on monitoring and alerting without actively engaging in response actions. They often leave the responsibility of incident response to the customer. MSSPs generally offer more passive, automated monitoring, which may not be sufficient to address sophisticated and rapidly evolving cyberthreats.
As a result, MDR has emerged as a comprehensive security offering that integrates advanced threat detection technologies, such as extended detection and response (XDR), with human expertise. This combination allows for a more holistic and effective approach to identifying and mitigating cyberthreats, providing organizations with a heightened level of protection in the ever-evolving threat landscape.
The Framework of MDR Services
The MDR framework can be broken down into three main areas: core components of MDR, technology and tools powering MDR, and the role of the security operations center (SOC) in MDR. The framework of MDR services is built on a foundation of core components that work together to provide a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity.
Advanced technologies and tools enhance the effectiveness of these services, while the SOC ensures that the organization is continuously protected from evolving threats.
Core Components of Managed Detection and Response
The core components of MDR services are crucial for establishing a strong and proactive cybersecurity posture. These components collaborate to offer a seamless and effective defense against cyberthreats.
Threat Hunting
Threat hunting is a proactive cybersecurity approach that involves actively and continuously searching for potential threats that may have bypassed traditional security measures. Instead of relying solely on automated systems, threat hunters leverage their expertise and knowledge to identify abnormal behavior and potential threats that have not been previously detected or classified.
This hands-on approach enables organizations to uncover sophisticated and stealthy threats at an early stage, minimizing their potential impact on the organization's security posture.
Incident Response
Incident response is a comprehensive and structured methodology for addressing and managing the aftermath of security incidents. This process involves the rapid identification of threats, followed by swift containment, eradication, and recovery efforts to minimize the impact of the attack.
The incident response team conducts in-depth analysis and collaborates with relevant stakeholders to ensure a coordinated and effective response. Additionally, measures are implemented to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future. A successful incident response plan not only minimizes the damage caused by the incident but also prioritizes the continuity of business operations.
Endpoint Detection
Endpoint detection is a critical cybersecurity measure that centers around the monitoring and protecting individual devices, including computers, mobile devices, and servers. Through continuous analysis of the activities and behaviors occurring on these endpoints, managed detection and response (MDR) services are able to identify and take action against potential security threats at the device level.
This approach is essential because endpoints are frequently the main objectives for cyberattackers seeking unauthorized access to the network.
Threat Intelligence and Analysis
Threat intelligence involves collecting and analyzing information about current and emerging threats. This intelligence is used to inform the detection and response strategies, ensuring they are up-to-date and effective against the latest threats. Analysis of threat intelligence helps in understanding the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by attackers, enabling more effective defense mechanisms.
Explore how MDR services can expand internal expertise, resources or technology to more effectively detect and respond to cybersecurity threats: What are Managed Detection and Response (MDR) Services?
Technology and Tools Powering MDR
MDR services leverage a variety of advanced technologies and tools to enhance their effectiveness. These technologies provide the necessary capabilities for monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats in real time.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
EDR solutions continuously monitor and analyze endpoint activities to detect suspicious behavior. EDR tools do the following:
- Collect data from endpoints
- Analyze it for signs of compromise
- Provide detailed insights into the nature and extent of threats
- Enable quick detection and response to attacks, minimizing potential damage
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM systems aggregate and analyze data from various sources across an organization’s IT infrastructure. By correlating events and identifying patterns, SIEM solutions help in detecting anomalies and potential threats. They provide a centralized view of the security landscape, making it easier to manage and respond to incidents.
Next-Generation Antivirus (NGAV)
NGAV goes beyond traditional antivirus solutions by using advanced techniques such as machine learning and behavioral analysis to detect and block sophisticated threats. NGAV solutions are designed to identify unknown threats and zero-day exploits that traditional antivirus systems might miss, providing an additional layer of protection.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
XDR integrates multiple security products into a cohesive system, providing a broader view of the threat landscape. By correlating data across endpoints, networks, and cloud environments, XDR enhances the ability to detect and respond to complex threats. This holistic approach improves the overall efficiency and effectiveness of threat detection and response efforts.
The Role of Security Operations Center (SOC) in MDR
The security operations center (SOC) is the heart of MDR services, acting as the command center for monitoring, detecting, and responding to security threats. The SOC is staffed by skilled security analysts and incident responders who work around the clock to protect the organization’s assets.
The SOC utilizes advanced tools and technologies to continuously monitor the organization’s IT environment, identify potential threats, and coordinate responses. By maintaining a vigilant watch over the network, the SOC ensures that any signs of compromise are quickly identified and addressed.
The SOC also plays a crucial role in threat hunting, incident response, and integrating threat intelligence into the organization’s security strategy.
Types of Detection and Response Solutions
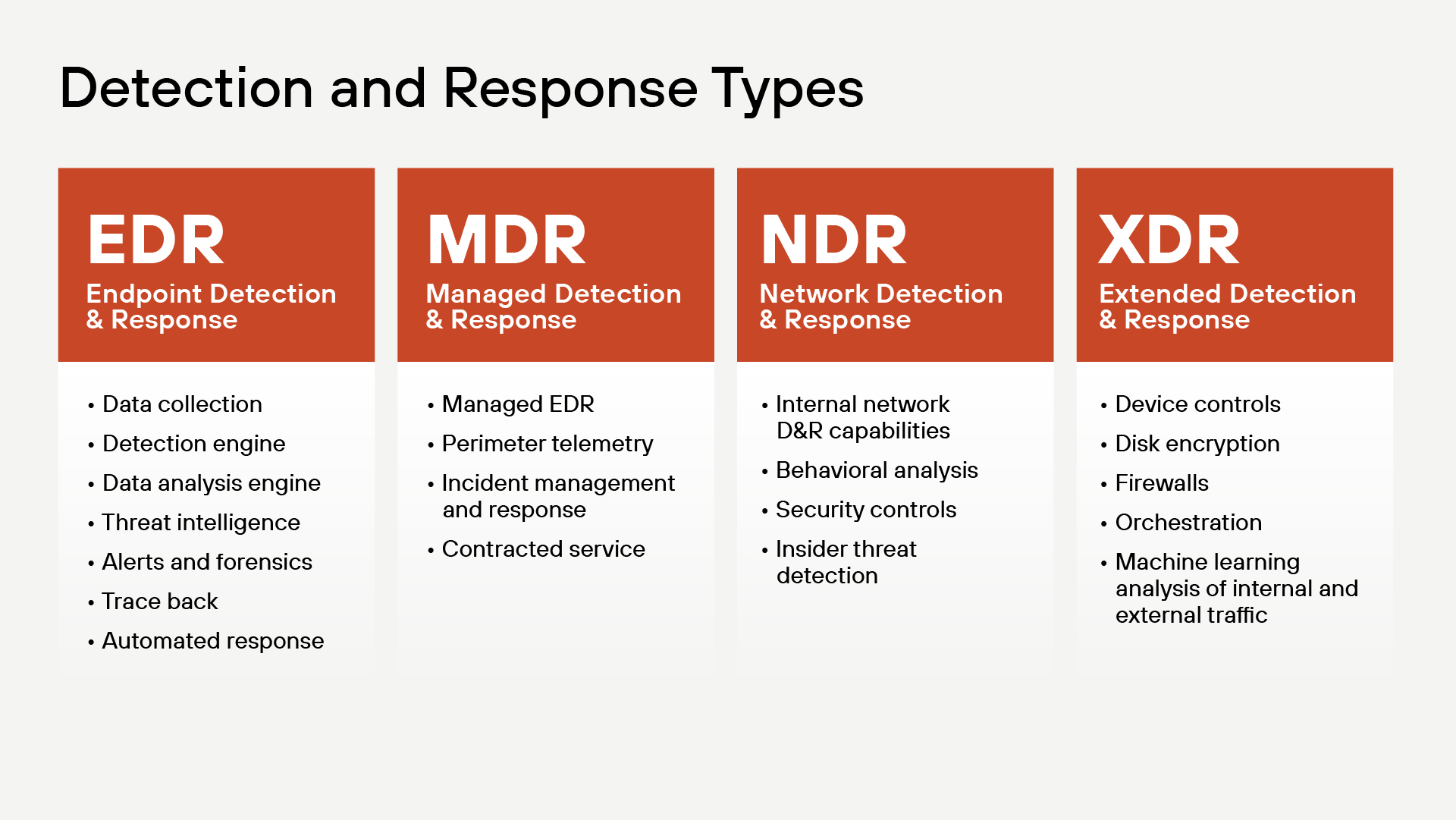
Organizations can choose from several detection and response approaches, each with distinct capabilities and focus areas:
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) focuses specifically on individual devices and endpoints. EDR solutions provide comprehensive data collection, sophisticated detection engines, and automated response capabilities at the device level. Key features include threat intelligence integration, detailed forensics, trace-back capabilities, and real-time alerts for endpoint activities.
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) builds upon EDR by adding managed services and human expertise. MDR providers offer managed EDR capabilities, perimeter telemetry monitoring, comprehensive incident management and response, and fully contracted security services. This approach combines technology with expert security analysts who actively monitor and respond to threats.
Network Detection and Response (NDR) specializes in monitoring internal network traffic and communications. NDR solutions excel at behavioral analysis of network patterns, implementing security controls at the network level, and detecting insider threats that may bypass endpoint protections. This approach provides visibility into lateral movement and network-based attacks.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) represents the most comprehensive approach, integrating multiple security layers into a unified platform. XDR solutions combine device controls, disk encryption, firewall management, and orchestration capabilities. They leverage machine learning to analyze both internal and external traffic, providing holistic visibility across the entire security infrastructure.
Each approach addresses different aspects of cybersecurity, and many organizations implement multiple solutions or choose XDR for its integrated capabilities.
MDR vs. EDR vs. MSSPs
Understanding the distinctions between managed detection and response (MDR), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and managed security service providers (MSSPs) is crucial. Each of these services offers unique capabilities and benefits, addressing different aspects of an organization's security needs. By clearly differentiating between these services, organizations can make informed decisions about their security strategies.
MDR Vs. EDR
While both MDR and EDR play critical roles in cybersecurity, they differ in scope and focus. MDR provides a broader, more integrated approach to threat detection and response, encompassing the entire IT environment, including endpoints, networks, and cloud infrastructure.
In contrast, EDR is specifically focused on endpoint security, offering deep visibility and protection for individual devices. MDR services often incorporate EDR capabilities as part of their overall strategy, providing a more comprehensive solution. EDR solutions provide visibility into endpoint activities and use advanced analytics to detect suspicious behavior.
Key features of EDR include:
- Endpoint monitoring: Continuous tracking of endpoint activities to identify signs of compromise.
- Behavioral analysis: Analyzing endpoint behavior to detect anomalies and potential threats.
- Automated response: Implementing automated actions to contain and remediate threats at the endpoint level.
- Forensics: Providing detailed insights into the nature and extent of endpoint attacks for post-incident analysis.
Dig into the differences between MDR and EDR: What is MDR vs EDR?
How MDR Services Extend Beyond Traditional MSSPs
MSSPs offer a range of security services to help organizations manage their security infrastructure and operations. These services typically include firewall management, intrusion detection and prevention, vulnerability assessments, and security monitoring. MSSPs provide valuable support in managing and maintaining security technologies, but their primary focus is on operational efficiency rather than proactive threat detection and response.
While MSSPs focus on managing and optimizing security technologies, MDR services prioritize threat detection and response, providing a more dynamic and proactive approach to cybersecurity. Organizations that require a higher level of threat detection and response capabilities will benefit from the comprehensive services offered by MDR.
Uncover the distinctions between MDR and MSSP by reading: What is MDR vs MSSP?: Key Differences.
Integration of MDR With In-House Security Teams
A collaborative approach for integrating MDR services with in-house security teams can significantly enhance an organization's overall security posture. By combining the proactive and comprehensive capabilities of MDR with the contextual knowledge and operational expertise of the in-house team, organizations can achieve a more resilient and effective cybersecurity posture. This collaboration leverages the strengths of both the MDR provider and the internal team.
Key Benefits of MDR integration include:
- Enhanced expertise: MDR services bring specialized skills and knowledge that complement the capabilities of the in-house team.
- 24/7 coverage: MDR provides round-the-clock monitoring and response, ensuring continuous protection even when the in-house team is off-duty.
- Scalability: MDR services can easily scale to meet the evolving security needs of the organization, providing additional resources and support as needed.
- Advanced threat detection: MDR uses cutting-edge technology and threat intelligence to detect sophisticated threats that may be beyond the capabilities of the in-house team.
Integration Strategies are as follows:
- Clear communication channels: Establishing clear lines of communication between the MDR provider and the in-house team ensures seamless collaboration and quick response to threats.
- Defined roles and responsibilities: Clearly defining the roles and responsibilities of both the MDR provider and the in-house team helps avoid duplication of efforts and ensures efficient resource use.
- Regular reporting and feedback: Regular reporting and feedback from the MDR provider help the in-house team stay informed about the security landscape and improve their own practices.
- Joint incident response plans: Developing joint incident response plans ensures that both the MDR provider and the in-house team can work together effectively during a security incident.
Implementing MDR
Implementing MDR involves careful consideration of various factors, a structured transition plan, and ongoing measurement of the MDR solution's effectiveness. It's important to outline the key considerations when choosing an MDR provider, the step-by-step process for transitioning to MDR services, and how to measure the effectiveness of the MDR solution.
Key Considerations When Choosing an MDR Provider
Choosing the right MDR provider is crucial to ensure that the service meets your organization's specific security needs. Here are the key factors to consider:
Expertise and Experience in Cybersecurity
When selecting a cybersecurity provider, it's important to consider their industry knowledge, certified professionals, and track record. Industry knowledge is crucial as different industries face unique security challenges, and a provider with relevant experience will be better equipped to address these challenges effectively.
Look for providers with certified security professionals who hold credentials such as CISSP, CISM, and CEH. These certifications indicate expertise and demonstrate the necessary skills and knowledge to handle advanced threats.
Additionally, assess the provider's track record in managing and responding to cyberthreats. Case studies, testimonials, and references can provide valuable insights into their performance and reliability, helping you make an informed decision.
Range and Depth of Security Services Offered
Your provider should offer a comprehensive range of services, including threat hunting, incident response, endpoint detection, and threat intelligence. A provider with a wide array of services can cover all aspects of security and provide comprehensive protection.
Additionally, it is important to verify that the provider uses advanced technologies such as endpoint detection and response (EDR), security information and event management (SIEM), next-generation antivirus (NGAV), and extended detection and response (XDR). These advanced technologies significantly enhance threat detection and response capabilities.
Moreover, the provider should be able to scale their services to match your organization's growth and evolving security needs, ensuring continuous and adaptable protection as your organization expands.
Customization and Flexibility in Security Solutions
Select a provider that offers customizable security solutions tailored to your organization's specific requirements, as one-size-fits-all solutions may not adequately address unique security challenges. Look for providers that offer flexible contract terms, allowing you to adjust services as needed. This flexibility ensures you can adapt to changing security landscapes without being locked into rigid agreements.
The MDR solution should seamlessly integrate with your existing security infrastructure and tools, ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing the effectiveness of your security operations.
Transitioning to MDR Services: Step-by-Step Process
Transitioning to MDR services requires a structured approach to ensure a smooth and effective implementation. The process involves several key steps.
Step 1: Assess Current Security Posture
The first step is to assess your current security posture. Conduct a thorough gap analysis to identify areas for improvement by evaluating your existing security tools, processes, and capabilities. Perform a risk assessment to understand your organization's specific threat landscape and prioritize areas needing immediate attention.
Step 2: Define Clear Objectives
Next, define clear objectives for what you want to achieve with MDR services, such as improved threat detection, faster incident response, or an enhanced overall security posture. Outline your specific requirements for the MDR provider, including the range of services, technologies, and integration needs.
Step 3: Select the Right Provider
Evaluate and shortlist potential providers based on key considerations such as expertise, service range, and flexibility. Conduct interviews, request proposals, and perform due diligence. If possible, run a proof of concept (PoC) to test the provider's capabilities and ensure they meet your requirements.
Step 4: Develop Implementation Plan
Develop a detailed implementation plan that outlines the steps, timelines, and resources needed for the transition. Define roles and responsibilities for both your internal team and the MDR provider, and establish a communication strategy to keep all stakeholders informed throughout the transition process.
Step 5: Execute
Execute the transition by working with the MDR provider to onboard their services, including integrating their technologies with your existing infrastructure. Provide training for your internal team to ensure they understand how to work with the MDR provider and utilize the new tools effectively.
Step 6: Continuously Monitor
Finally, continuously monitor the MDR services to ensure they are performing as expected. Review reports and metrics provided by the MDR provider regularly and work with them to optimize the services and address any issues or gaps.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Your MDR Solution
Measuring the effectiveness of your MDR solution is essential to ensure it delivers the desired security outcomes. Here are key metrics and methods to evaluate the performance of your MDR services:
Detection and Response Metrics
- Mean Time to Detect (MTTD): Measure the average time taken to detect a threat. Shorter MTTD indicates more effective threat detection capabilities.
- Mean Time to Respond (MTTR): Measure the average time taken to respond to and mitigate a threat. Faster MTTR demonstrates efficient incident response processes.
Threat Intelligence and Analysis Metrics
- False Positive Rate: Track the number of false positives generated by the MDR solution. A lower false positive rate indicates more accurate threat detection.
- Threat Coverage: Evaluate the range and types of threats detected by the MDR solution. Comprehensive threat coverage ensures robust protection against various attack vectors.
Incident Response Metrics
- Incident Resolution Time: Measure the time taken to fully resolve security incidents. Quick resolution times minimize the impact on business operations.
- Post-Incident Analysis: Conduct post-incident analyses to assess the effectiveness of the response and identify areas for improvement.
Customer Satisfaction Metrics
- Feedback and Surveys: Collect feedback from internal stakeholders to gauge their satisfaction with the MDR services. Surveys and interviews can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and areas for improvement.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Review the MDR provider's adherence to SLAs and their performance against agreed-upon metrics.
Continuous Improvement
- Regular Reviews: Schedule regular reviews with the MDR provider to discuss performance, address issues, and explore opportunities for improvement.
- Adaptation to New Threats: Ensure the MDR provider continuously updates their technologies and strategies to adapt to new and emerging threats.
The Impact of MDR on Modern Cybersecurity Strategies
MDR services are now essential in modern cybersecurity strategies. They offer a proactive and comprehensive approach to threat detection and response. By integrating advanced technologies with human expertise, MDR significantly enhances an organization’s security posture.
MDR improves security by using continuous monitoring and advanced analytics to identify and mitigate threats before they cause harm. Tools like EDR, SIEM, and XDR continuously scan for anomalies, while expert threat hunters actively search for hidden threats. This proactive approach minimizes damage and disruption. Additionally, MDR excels in incident response by ensuring efficient threat handling, stakeholder communication, forensic analysis, and post-incident reviews.
Threat intelligence is crucial in shaping security strategies by providing insights into current and emerging threats. MDR providers integrate real-time threat data from various sources to inform their detection and response strategies, enabling organizations to prioritize efforts based on the most relevant threats. This intelligence helps create resilient and adaptive security policies, ensuring alignment with the current threat environment.
MDR services tackle alert fatigue by filtering and prioritizing alerts, allowing security teams to focus on genuine threats. Advanced machine learning algorithms and behavioral analysis reduce false positives, streamlining the incident response process. This leads to faster and more effective threat mitigation, minimizing the impact of cyberattacks, enhancing overall security, and ensuring business continuity.
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) FAQs
- Implementing Data Management Strategies: Using data filtering and prioritization techniques to manage and make sense of the large volumes of data.
- Proper Configuration: Working with EDR vendors to ensure tools are properly configured and tailored to the specific needs of the organization.
- Training and Hiring: Investing in training for existing staff or hiring skilled cybersecurity professionals to effectively manage and utilize EDR solutions.
- Automating Responses: Leveraging the automated response features of EDR tools to handle routine threats, freeing up human resources for more complex incidents.