- What Is Access Control?
-
What Is Identity Visibility and Intelligence (IVIP)?
- The Identity Visibility Crisis
- Understanding IVIP: Definition and Core Concepts
- Why IVIP Emerged Now
- What IVIP Actually Does
- IVIP Within the Identity Fabric Architecture
- IVIP vs. Adjacent Technologies
- Real-World Use Cases and Applications
- Implementation Considerations and Architecture
- Market Maturity and Adoption Roadmap
- Identity Visibility and Intelligence Platforms (IVIP) FAQs
- What Is Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM)?
-
What is Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM)?
- What Identity Security Posture Management Is and Why It Emerged
- The Identity Attack Surface in Modern Enterprises
- Core Capabilities of ISPM Platforms
- How ISPM Differs from Adjacent Technologies
- ISPM Architecture and Technical Implementation
- Key Use Cases and Operational Workflows
- ISPM Implementation Strategy
- Common Identity Posture Risks ISPM Addresses
- Measuring and Improving Identity Security Posture
- The Future of Identity Security Posture Management
- ISPM FAQs
- What Is Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
- What is the Evolution of Multifactor Authentication
- What Is the Principle of Least Privilege?
-
What Is Multifactor Authentication?
- Multifactor Authentication Explained
- Why Multifactor Authentication Is Crucial
- How Multifactor Authentication Works
- Authentication Factors and Methods
- MFA vs. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Implementing Multifactor Authentication: Best Practices
- MFA Deployment Considerations
- Common MFA Security Weaknesses and Mitigations
- MFA Policy, User Experience, and Compliance
- Advanced MFA Concepts: Adaptive and AI-Enhanced Authentication
- Real-World MFA Examples
- The Future of MFA: Emerging Trends and Innovations
- Multifactor Authentication FAQs
- What Is Access Management?
- What is BeyondCorp?
- What Is Least Privilege Access?
- What are MFA Examples and Methods?
What is Multifactor Authentication (MFA) Implementation?
Multifactor authentication (MFA) implementation involves integrating a security system that requires users to verify their identity through two or more authentication factors, such as passwords, biometrics, or one-time codes. Unlike single-factor authentication, which typically relies only on a password, MFA employs at least two independent credentials:
- Something the user knows (like a password)
- Something the user has (such as a smartphone for an OTP)
- Something the user is (biometrics such as fingerprints or facial recognition).
This enhances access control and protects sensitive data by adding layers of security, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
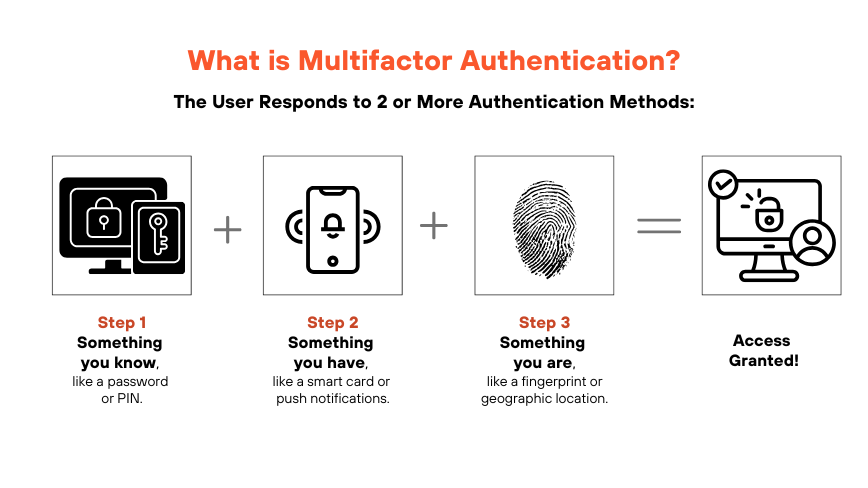
Figure 1: What is MultiFactor Authentication?
Why MFA Implementation is Important
In today's digital landscape, cybersecurity threats are more sophisticated and pervasive than ever, making it crucial for organizations to implement comprehensive security measures. Multifactor authentication (MFA) is vital in fortifying cybersecurity by drastically reducing the chances of unauthorized access.
With cybercriminals constantly evolving their tactics, relying on a single layer of security, like a password, is no longer sufficient. This layered approach enhances security by making it more challenging for attackers to gain entry. It also provides peace of mind to businesses and their clients, knowing that their information is protected by more than conventional means.
Furthermore, MFA is critical in meeting compliance requirements and standards set forth by various regulatory bodies. It ensures that organizations safeguard their data and adhere to best practices in information security. By integrating MFA, businesses significantly boost their resilience against data breaches and unauthorized account access, protecting their reputations and financial stability.
Key Advantages of Implementing MFA
Implementing MFA offers numerous key advantages that significantly strengthen security across various digital platforms:
- Mitigates the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access effectively.
- Supports compliance with industry regulations and standards, such as GDPR and PCI DSS.
- Assists in avoiding penalties and fines associated with non-compliance.
- Maintains trust and credibility with clients and partners.
- Requires multiple verification methods, making it exceedingly difficult for attackers to access sensitive information.
- Acts as a deterrent against potential cyber attacks, as the complexity discourages attackers.
- Enhances overall user experience by providing peace of mind.
- Ensures business continuity and safeguards valuable data assets.
Planning Your MFA Implementation Strategy
Planning a strategy for MFA implementation is vital for ensuring seamless integration that addresses an organization's security needs. A well-executed planning process can establish a resilient security foundation that adapts to the evolving threat landscape.
Step 1: Assessing Organizational Needs
Assessing organizational needs is the foundational step in implementing MFA. This process involves thoroughly evaluating the current security landscape and identifying specific vulnerabilities that MFA can mitigate. Key considerations during this assessment include:
- The types of data that require protection.
- The sensitivity of this data.
- The potential threats unique to the organization’s industry.
- A solid understanding of the existing IT infrastructure and how it integrates with new MFA solutions to ensure compatibility and minimize disruptions during implementation.
- The workforce's geographical distribution and technological proficiency are needed to select authentication methods that are user-friendly and feasible for widespread adoption.
Engaging Stakeholders
Involving stakeholders from different departments in discussions about security priorities is essential to ensure that the MFA implementation aligns with organizational goals and addresses key security issues. The assessment phase aims to balance the likelihood of specific threats with the need to maintain core operations. This requires IT security leaders to collaborate with stakeholders.
These discussions should focus on adopting a blanket MFA approach for all users and systems or a more targeted MFA for specific users or resources. Many organizations find that a combined MFA approach is often the most effective solution.
Step 2: Selecting the Right MFA Methods
Choosing the correct MFA methods is crucial for balancing security needs with user experience and ensuring effective deployment across your organization. The following tips can guide the process:
- Analyze Organizational Needs and Threats: To choose the most effective MFA methods, understand your organization's specific requirements and potential security threats.
- Balance Security with User Experience: To promote widespread adoption, select MFA methods that provide comprehensive security while ensuring user convenience.
- Evaluate Device Compatibility: Check if your organization's devices support advanced authentication methods, such as biometrics (e.g., fingerprints and facial recognition).
- Consider User Demographics: When deciding between push notifications, hardware tokens, or text codes, consider user factors such as age, tech proficiency, and environment.
- Collaborate with IT Teams: Work closely with IT teams to ensure chosen MFA solutions integrate smoothly with existing systems and processes.
- Engage End-Users Early: Gather end-user feedback to identify potential usability issues and select methods that enhance security and user satisfaction.
Step 3: Creating Comprehensive MFA Policies
Creating comprehensive MFA policies is a critical step that ensures a cohesive framework for security practices across the organization. These policies should establish clear guidelines for implementing and managing MFA systems to ensure consistent application and adherence among users.
Define Scope and Objectives
Start by defining the scope and objectives of your MFA approach, ensuring they align with your organization's security goals and compliance requirements. Then, clearly articulate user roles and responsibilities in the process, addressing how employees will be authenticated and the types of authentication methods to be used.
Incorporate Contingency Plans
The policies should incorporate contingency plans for inevitable scenarios such as lost authentication devices or system failures to maintain uninterrupted security flow. Allow room for flexibility by including adaptive strategies to accommodate technological advancements, ensuring your policy remains comprehensive and relevant.
Review and Update
Regularly reviewing and updating policies is critical to reflect evolving security landscapes and will help your organization stay ahead of potential threats and uphold strong security measures.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing MFA
Implementing MFA requires a well-structured approach to ensure its effectiveness in enhancing security while maintaining user convenience.
Preparing for Deployment
Preparing for MFA deployment involves aligning technical setups with previously identified security needs and engaging stakeholders from all departments to clarify roles and expectations. A solid communication plan is vital to inform employees about the changes, MFA benefits, and responsibilities.
Training sessions should be organized to give staff hands-on experience with the new system and address potential tech proficiency gaps. Reviewing existing IT infrastructure is also critical to identifying necessary upgrades and ensuring seamless MFA integration without disrupting daily operations. This thorough preparation is essential for a successful transition to improved security.
Engaging and Educating Employees
A knowledgeable workforce strengthens security since employees are often the first line of defense against breaches. The following suggestions will assist in their education:
- Explain MFA's purpose and benefits to ensure all staff understand how it protects organizational and personal data.
- Provide hands-on training to improve user adoption as employees get comfortable with various authentication methods.
- Establish a feedback loop to allow employees to share their experiences and challenges, leading to better deployment and usability.
- Maintain open communication to foster a security-focused culture where employees stay alert and adopt security best practices beyond MFA.
Technical Setup and Configuration
MFA's technical setup and configuration involves configuring the MFA system to integrate seamlessly with the organization's existing IT infrastructure without compromising performance:
- Confirm that all necessary hardware and software components are compatible with the selected MFA solutions.
- Conduct thorough testing to identify any potential issues that may arise during or after implementation.
- Examine and configure network settings properly to prevent disruptions and ensure reliable connectivity for authentication processes.
- Collaborate with IT teams at this stage, as they can provide insights into system requirements and offer technical expertise to navigate potential challenges.
- Document all procedures and setups as a valuable reference for troubleshooting and future updates.
Overcoming Challenges in MFA Implementation
Addressing the challenges of implementing MFA requires a strategic approach to ensure a secure and smooth transition. By proactively addressing these challenges, organizations can establish a resilient framework for an effective MFA rollout while reinforcing their security posture amid evolving cyber threats.
Common Barriers
Resistance to Change
One of the primary challenges is resistance to change, as employees may be hesitant or reluctant to adopt new security measures due to perceived complexity or inconvenience. To overcome this, it is essential to clearly communicate MFA's benefits and necessity, offering comprehensive training and support to ease the transition.
Technical Limitations
Another significant barrier can be technical limitations, where existing IT infrastructure may not fully support new MFA solutions, leading to potential integration issues. Addressing these requires thoroughly assessing current systems and investing in upgrades to accommodate the MFA deployment.
Cost Considerations
Cost considerations can also pose a hurdle, as implementing resilient MFA measures involves investment in technology, training, and user education. Organizations should prepare a budget for upfront expenses and ongoing support costs.
Ensuring Compatibility with Existing Systems
Compatibility is crucial for implementing multi-factor authentication. Challenges can occur when legacy systems or outdated software don't support advanced methods like biometrics or tokens.
Organizations should assess their IT infrastructure to identify issues hindering MFA deployment. Collaborating with IT teams is essential, as their knowledge of system operations can inform necessary upgrades. Choosing adaptable MFA solutions that integrate easily can help bridge compatibility gaps, ensuring a smooth transition that enhances security and maximizes MFA adoption.
Managing Cost Implications
Implementing MFA involves considerable investment, making the management of the following cost implications a critical factor for organizations:
- Initial expenses related to purchasing and deploying technology, training staff, and potentially upgrading existing systems.
- Recurring costs related to ongoing maintenance, support, and updates to authentication methods.
To manage these expenses, businesses can explore scalable solutions that align with their budget, ensuring they pay only for the resources they need as their security requirements evolve. Open communication with vendors can also help negotiate favorable terms or payment plans, helping organizations maximize value while maintaining strong security.
Best Practices for Maintaining Effective MFA
- Continuously Monitor for Threats: Regularly check for signs of unauthorized access attempts to identify and mitigate potential security threats promptly.
- Update Authentication Methods Regularly: Keep MFA systems aligned with evolving cyber threats by incorporating the latest advancements in authentication technologies.
- Leverage Emerging Technologies: Adopt advanced biometrics or adaptive authentication innovations to enhance security and improve user experience.
- Engage Users for Feedback: Involve users in gathering insights and refining the system for better functionality and user satisfaction.
- Evaluate MFA Success Metrics: Track metrics such as user compliance and system effectiveness to validate your strategy and identify areas for improvement.
- Stay Proactive in Security Planning: Anticipate future security needs and prepare for new developments to ensure MFA remains a strong defense against unauthorized access.
Evaluating the Success of MFA Deployment
Evaluating the success of MFA deployment involves a comprehensive analysis of technical effectiveness and user compliance. Organizations can measure MFA effectiveness by:
- Tracking metrics such as the reduction in unauthorized access attempts and the successful prevention of security breaches.
- Gathering user feedback that provides insights into potential usability challenges and helps refine the system for better functionality and satisfaction.
- Prepare for future security developments by staying informed about emerging technologies and threats, ensuring the MFA system remains comprehensive and adaptable.
- Continuously monitoring and analyzing security logs and user behavior can uncover areas that need reinforcement, cementing the organization's proactive stance in safeguarding its digital assets.